Status of Human Footprint and Native Vegetation
Summary of the status of human footprint and native vegetation in Tolko's Northern Operating Area, circa 2021.
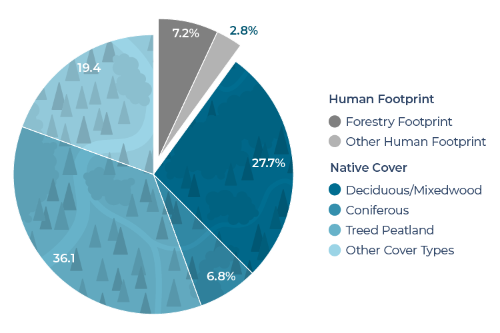
Total human footprint
- Of this total, the forestry footprint was 7.2%, decreasing to 5.3% when accounting for the regeneration of harvested stands.
- Energy (2.1%) was the next most common human footprint type, while the remaining footprint types combined covered <1% of the region.
Undisturbed Native Vegetation
- Undisturbed upland stand types, where forest harvest takes place, cover 34.5% of the land base.
- This includes deciduous (23.2%), White Spruce (4.7%), mixedwood (4.5%), and pine (2.1%).
Introduction
The extent of human land use in a given area is collectively defined as human footprint.
-
The expansion of human footprint and the disturbance of native ecosystems is one of the key threats to biodiversity[1]. Responsible development depends on understanding the complex interactions between human activities, habitats, and species.
- In Tolko’s Northern Operating Area, much of the region is managed for timber production. But oil and gas exploration and development are also common features across the landscape, particularly linear disturbance in the form of seismic lines.
- Measuring human footprint—such as forest harvest areas, well sites, roads, and seismic lines—is an important land-use planning tool to monitor the status of landscapes.
- Further, understanding how human land use is affecting different ecosystems is important to support sustainable, evidence-based land-use decisions.
In this section, we summarize the current human footprint and native vegetation in Tolko’s Northern Operating Area.
Forestry footprint is the most common footprint in the Northern Operating Area.

Energy footprint (e.g., well sites, seismic lines, and pipelines) is the second most common footprint type.

Large areas of the Northern Operating Area remain undisturbed.
Results
Status of Human Footprint
The total human footprint in the Northern Operating Area was:
Highlights
- Forestry was the largest human footprint in Tolko’s Northern Operating Area, covering 7.2% of the region; forestry footprint is 5.3% when ecological recovery of harvested areas is considered.
- After forestry, energy was the next most common human footprint, covering 2.1% of the Northern Operating Area.
- The remaining human footprint types each covered less than 1% of the region: transportation (0.5%), urban/industrial (0.1%), human-created waterbodies (0.1%), and agriculture (0.05%).
View as Graph
View as Table
Status of Human Footprint. Summary of per cent (%) area of human footprint broken down by category for Tolko’s Northern Operating Area. Total human footprint includes all categories other than Forestry, Net. Hover over the bar or legend (in graph view) to view the per cent area of each footprint type.
Results
Status of Native Vegetation
- In the Northern Operating Area, 34.5% of the land base is covered by undisturbed upland forest types, deciduous being the most common at 23.2%, with White Spruce (4.7%), mixedwood (4.5%), and pine (2.1%) each covering <5% of the land base.
- Undisturbed lowland forest types are also common in the Northern Operating Area, including Black Spruce (19.7%) and treed fen (16.4%).
- Non-forested vegetation covered 16.8% of the region, and 2.6% of the area is open water (rivers and lakes).

Tolko harvests coniferous trees in the Northern Operating Area.
View as Graph
View as Table
Status of Vegetation Types. Per cent (%) area, circa 2021, of vegetation types in Tolko’s Northern Operating Area. Hover over the bar or legend (in graph view) to view the per cent area of each vegetation type.
References
Sanderson, E.W., M. Jaiteh, M.A. Levy, K.H. Redford, A.V. Wannebo, and G. Wolmer. 2002. The human footprint and the last of the wild. Bioscience 52(10):891-904.




